On March 18th Siegfried R. Waldvogel appeard as one of the speakers in the webinar "Driving Change – How Green Chemistry and Digitalisation lead the way to a Sustainable Economy" during the EU Industry Week 2021. Siegfried R. Waldvogel represented the Johannes Gutenberg University, SusInnoScience and ESy-Labs in the field of electroorganic, green and sustainable chemistry.
Further information can be found here.
The newspaper Zeit has published an article about the Top-level and High-potential Research Areas of JGU including SusInnoScience in their magazine Zeit Campus.
The article can be found here.
Sustainable chemistry as the key to innovation in resource-efficient science in the Anthropocene
The establishment of sustainable innovations and contributions to a circular economy represent the most important challenges for a future innovation-driven industrial society. Moreover, avoiding fossil carbon feedstock currently represents the most urgent issue within the Anthropocene. Here, sustainable chemical solutions open up a whole range of attractive options for challenges in raw material supply, energy conversion, chemical processes, and in materials science. The primary goal of this research initiative is the use of renewable raw materials, non-critical elements and the efficient use of renewable energies for the activation as well as conversion.
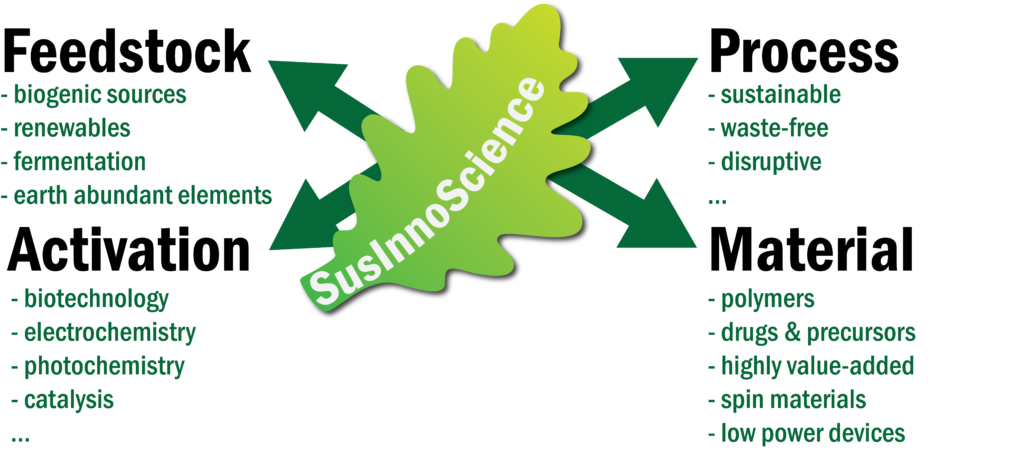
To achieve this goal, the Faculties 09 (Chemistry) and 10 (Biology) are working closely together. Biotransformations such as microbial activations and conversions will be combined with cutting-edge technologies such as electrosynthesis and photocatalysis. Critical elements, such as valuable and rare metals, are exchanged. Fossil and limited resources are systematically avoided. Instead, waste streams and renewable feedstocks are used as carbon sources and common elements are used. Sustainable, green and as waste-free as possible processes, a circular economy, as well as innovative disruptive scientific and technological advances are targeted.
Leading PIs
Prof. Dr. Pol Besenius
Prof. Dr. Katja Heinze
Prof. Dr. Carsten Streb (Speaker)
Prof. Dr. Eckhard Thines (Co-Speaker)

